2. 农业部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 青岛 266071;
3. 中国水产科学研究院东海水产研究所 上海 20009
2. Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Qingdao 266071;
3. East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Shanghai 200090
银鲳(Pampus argenteus)属硬骨鱼纲(Osteichthyes)、鲈形目(Perciformes)、鲳科(Stromateidae)、鲳属(Pampus),是近海暖水性鱼类,在我国渤海、黄海、东海和南海等海区皆有分布(尹飞等, 2011; 徐善良等, 2012; 秦玉等, 20131))。银鲳俗称镜鱼、平鱼或车片鱼,鱼体呈卵圆形,体形侧扁,体背面与体腹面狭窄,体长为体高的1.4–1.6倍,头长为吻长的3.8–4.8倍;4鼻孔,口小,上下颌具细小牙一行;体被银白色的细小圆鳞,易脱落,头部除两颌及吻部外全部被鳞;背鳍隆起呈镰刀状,臀鳍与背鳍对称且同形(图 1)。银鲳繁殖期在每年的5–6月,受精卵为浮性球形卵。银鲳具有生长快、个体大、肉质细嫩鲜美等特点,且有较高的经济价值与营养价值(赵峰等, 2009),是我国重要的海洋经济鱼类,但由于过度捕捞和生存环境受到破坏,其资源量正在逐年下降(李建生等, 2014)。目前,国内外对银鲳的研究主要集中在分类、资源评估、胚胎发育、繁殖习性和环境胁迫等(刘静等, 2002; 赵峰等, 2011; 施兆鸿等, 2016; Almatar et al, 2004),有关染色体方面的研究还未见报道,仅有淡水白鲳(Colossoma brachypomum)和卵形鲳鲹(Trachinotus ovatus)(白俊杰等, 1988; 舒琥等, 2007)的染色体核型分析的相关报道。银鲳作为新开发的工厂化养殖品种,研究其染色体核型对银鲳的遗传、变异、分类、系统演化和育种等都有重要意义。本研究以银鲳鳃组织为材料,观察银鲳的染色体及其核型,以期为银鲳遗传育种的研究提供理论基础。
1) Qin Y. Development of palymorphic mierosatellites for Pampus argenteus and its analysis on population genetic structure. Master´s Thesis of Zhejiang Ocean University, 2013 [秦玉.银鲳微卫星标记开发及群体遗传结构分析.浙江海洋学院硕士研究生学位论文, 2013]

|
图 1 银鲳 Figure 1 Pampus argenteus |
实验于2016年7月在山东青岛金沙滩水产开发有限公司进行,所用银鲳为70–80日龄,体长范围为7–9 cm。
1.2 染色体标本制备染色体标本的制备参照半滑舌鳎(Cynoglossus semilaevis)鱼苗染色体标本制备方法(周丽青等, 2005),略作修改,将银鲳置于秋水仙素终浓度为0.005%的海水中暂养4 h,设置3个平行组,每组10尾银鲳。
每组取3尾银鲳,剪取鳃组织,置于10 ml KCl溶液(0.0375 mol/L)中,低渗1 h,再将鳃组织转移至现配制预冷的卡诺氏(Carnoy)液(甲醇:冰醋酸=3:1)中,每隔30 min更换1次固定液,重复3次。固定鳃组织4℃保存过夜,次日将固定的鳃组织用50%冰醋酸解离约10 min,用滴管吹打加速解离,挑去未解离的鳃组织,吸取解离液采用热滴片法制备染色体标本。每尾鱼制备4张滴片,用10% Giemsa染色40 min,自来水冲洗,晾干并用100倍油镜镜检。
1.3 核型分析与比较染色体核型分析参考波纹唇鱼(Cheilihus uhdulatus)的染色体分析方法(周丽青等, 2010),略作修改。从制备的滴片中选取轮廓清晰的染色体中期分裂相进行染色体计数(周丽青等, 2005),再从中选取染色体收缩适中且分散最清晰的10个中期分裂相进行显微拍照,经放大打印后,描绘染色体轮廓进行核型分析,并计算相对长度和臂比。
相对长度=(实测染色体长度/全部染色体长度总和)×100;
臂比=长臂长度/短臂长度;
求出它们的平均值和标准差,按Levan等(1964)确定的标准进行染色体分类,得出银鲳的染色体核型公式。
2 结果 2.1 银鲳染色体数目的确定实验结果显示,通过热滴法制备的9尾银鲳的染色体标本,均观测到了染色体中期分裂相(图 2-a),未见有异形性染色体,统计清晰分裂相120个,并对银鲳二倍体中期分裂相进行染色体计数,结果列于表 1。由表 1可见,染色体数为2n=48占71.6%,确定染色体众数为48。
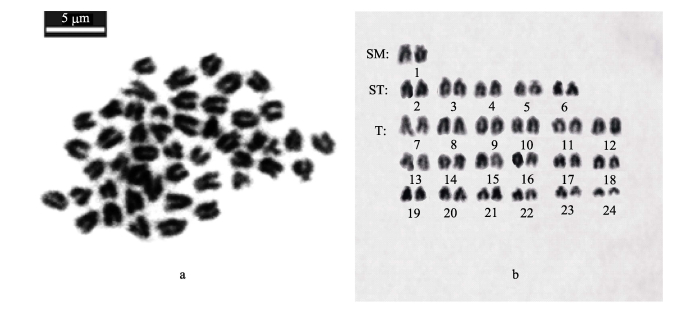
|
图 2 银鲳中期分裂相染色体及核型 Figure 2 The metaphase chromosome and karyotype of P. argenteus a.具有同型染色体银鲳的中期分裂相染色体;b.具有同型染色体银鲳的染色体核型 a. The mataphase chromosomes of P. argenteus with homotypic sex chromosomes; b. The karyotype of P. argenteus with homotypic sex chromosome |
|
|
表 1 银鲳二倍体染色体计数 Table 1 Counts of the diploid chromosome in P. argenteus |
银鲳染色体相对长度和臂比值统计结果见表 2。银鲳所有染色体都为同型染色体(图 2-b)。根据Levan等(1964)方法进行染色体分类,1号染色体臂比值在1.67–2.90范围内,属亚中部着丝粒染色体;2–6号染色体臂比值在3.0–7.0范围内,属亚端部着丝粒染色体;7–24号染色体臂比值 > 7.0。因此,确认银鲳染色体核型为2n=2SM+10ST+36T,并且部分染色体带有随体。
|
|
表 2 银鲳中期分裂相染色体相对长度和臂比值(平均值±标准差) Table 2 The relative length and arm ratio of metaphase chromosome in P. argenteus (Mean±SD) |
已知的海水鱼类染色体核型研究中,常见的染色体制备方法有外周血淋巴细胞培养、血细胞培养、鳞片培养、鳍条再生组织培养、肾细胞培养和胚胎培养等(马纲, 1996; 杨效文等, 2000),多以细胞分裂增生能力较强的器官组织为实验样本制备标本。最常用的方法是注射植物血凝素(PHA)体内培养肾细胞制片法(林义浩, 1982; 舒琥等, 2010),而银鲳的体表细小鳞片容易脱落,且对外界敏感且反抗激烈,当对其捞取进行实验操作时,容易受惊吓后剧烈游动、擦伤等导致体被细小鳞片脱落或体表受伤死亡。因此,向体内注射PHA或秋水仙素等离水实验操作均会对银鲳造成较大物理伤害,导致银鲳活力低下甚至过早死亡,不利于制备和获得中期分裂相。因此,常用的染色体制备方法不适用于银鲳。本研究首先让银鲳在含0.005%浓度秋水仙素的海水中游泳4 h,然后直接活体取鳃组织样本,该方法避免了对银鲳离水实验操作造成的物理伤害,确保银鲳在活力正常的前提下获得实验样本。另外,鳃作为鱼的呼吸器官,与水体直接接触,相比鳍、头肾等其他器官,鳃组织内的血液与水体的交换率更高,可以更好地发挥秋水仙素的作用,因此,本研究通过改良秋水仙素处理方式和取材方法,获得大量染色体形态好且分散好的银鲳中期分裂相。
研究鱼类染色体的多样性,对生物进化、变异与遗传都有重要的参考价值,而且对鱼类的分类、进化和不同鱼种的相关性也有重要意义,可为鱼类遗传育种提供细胞遗传学依据(Poltev, 2008),也为鱼类工厂化养殖的种质标准评定提供参考。目前,已有核型报道的海洋鱼类中,2n=48的核型数目占72%,鲈形目占大多数(朱香萍等, 2007; 赵金良, 2000),如七带石斑鱼(Epihephelus septemfasciatus) 2n=48(钟声平等, 2010)、卵形鲳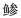
Gosline(1971)将真骨鱼类划分为低位类、中位类和高位类3个演化类群,并在此基础上,日本学者小岛吉雄(1979)认为,越处于上位类群,染色体数目变异范围分布越收敛,端部着丝点染色体越多,臂数越少。由银鲳染色体组型可知,其臂数NF=50,符合典型的高位类群鱼类核型特征。从进化角度讲,臂数的变化是从低位类群到高位类群表现为逐渐升高的趋势(李康等, 1984),即中部或亚中部着丝点染色体的增加代表着进化的趋势,由此可以说明,银鲳染色体核型是相对进化类型。其具体的进化程度有待进一步研究。
| Almatar SM, Lone KP, Abu-Rezq TS, et al. Spawning frequency, fecundity, egg weight and spawning type of silver pomfret, Pampus argenteus, (Euphrasen) (Stromateidae), in Kuwait waters. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2004, 20(3): 176-188 DOI:10.1111/jai.2004.20.issue-3 | |
| Bai JJ, Ma ZB. The karyotype of freshwater spadefish Colossoma brachypomum. Freshwater Fisheries, 1988(3): 9 [白俊杰, 马仲波. 淡水白鲳(Colossoma brachypomum)染色体组型分析. 淡水渔业, 1988(3): 9] | |
| Gosline WA. Functional morphology and classification of teleostean fishes. University Press of Hawaii, 1971. | |
| Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas, 1964, 52(2): 201-220 | |
| Li JS, Hu F, Yan LP. Study on the rational utilization of Pampus argenteus resources in the East China Sea region. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(8): 1420-1429 DOI:10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.08.014 [李建生, 胡芬, 严利平. 东海区银鲳资源合理利用的研究. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(8): 1420-1429] | |
Li K, Gui JF, Hong YH, et al. Studies on the karyotypes of Chinese cyprinid fishes. V. Karyotypes of species of Gobionid fishes.
Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science), 1984(3): 115-124 [李康, 桂建芳, 洪云汉, 等. 中国鲤科鱼类染色体组型的研究-V.  亚科10种鱼的染色体组型.
武汉大学学报(自然科学版), 1984(3): 115-124] 亚科10种鱼的染色体组型.
武汉大学学报(自然科学版), 1984(3): 115-124]
|
|
| Lin YH. A PHA injection method in vivo for the rapid obtainment of large numbers of metaphase figures from kideny cells of teleosts. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1982, 6(3): 201-208 [林义浩. 快速获得大量鱼类肾细胞中期分裂相的PHA体内注射法. 水产学报, 1982, 6(3): 201-208] | |
| Liu J, Li CS, Li XS. Studies on Chinese pomfret fishes of the genus Pampus. Studia Marina Sinica, 2002(44): 240-252 [刘静, 李春生, 李显森. 中国鲳属鱼类的分类研究. 海洋科学集刊, 2002(44): 240-252] | |
| Ma G. The research progress in chromosome pattern and numerical variation of freshwater fish in China. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 1996(3): 77-80 [马纲. 中国淡水鱼类染色体形态及数目变异的研究进展. 甘肃科学学报, 1996(3): 77-80] | |
| Poltev YN. Some issues related to reproduction of Pacific cod, Gadus macrocephalus in waters of the eastern coast of the northern Kuril Islands and the southern extremity of Kamchatka. Journal of Ichthyology, 2008, 48(4): 345-355 DOI:10.1134/S0032945208040073 | |
| Shi ZH, Xie MM, Peng SM, et al. Effects of temperature stress on activities of digestive enzymes and serum biochemical indices of Pampus argenteus juveniles. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2016, 37(5): 30-36 [施兆鸿, 谢明媚, 彭士明, 等. 温度胁迫对银鲳(Pampus argenteus)幼鱼消化酶活性及血清生化指标的影响. 渔业科学进展, 2016, 37(5): 30-36] | |
| Shu H, Cai XY, Liu F, et al. Karyotypes analysis for three species of Tetraodontiformes fishes. Chinese Journal of Zooloogy, 2010, 45(2): 101-106 [舒琥, 蔡晓阅, 刘锋, 等. 鲀形目3种鱼的染色体组型分析. 动物学杂志, 2010, 45(2): 101-106] | |
| Shu H, He ML, Zhang HF, et al. Study on the karyotyre in the Trachinotus ovatus. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 6(2): 23-25 [舒琥, 何敏莲, 张海发, 等. 卵形鲳鲹染色体组型研究. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 6(2): 23-25] | |
| Xiao DJX. Aquatic biology and genetic breeding. Tokyo: 1979: 46-62. [小岛吉雄. 水生生物及遗传育种. 东京: 水交出版社, 1979: 46-62.] | |
| Xu SL, Wang DL, Xu JL, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in muscle of Pampus argenteus, P. cinereus and P. sinensis from the East China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(4): 775-782 DOI:10.11693/hyhz201204014014 [徐善良, 王丹丽, 徐继林, 等. 东海银鲳(Pampus argenteus)、灰鲳(P. cinereus)和中国鲳(P. sinensis)肌肉主要营养成分分析与评价. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(4): 775-782] | |
| Yang XW, Zhang SF, Zhang XY. Karyotypes of green peach aphids from different host plants. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2000, 6(1): 56-60 [杨效文, 张素方, 张孝羲. 不同寄主植物上烟蚜的染色体组型研究. 应用与环境生物学报, 2000, 6(1): 56-60] | |
| Yin F, Sun P, Peng SM, et al. Effects of low salinity stress on the antioxidant enzyme activities in juvenile Pampus argenteus liver and the APTase activities in its gill and kidney. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(4): 1059-1066 [尹飞, 孙鹏, 彭士明, 等. 低盐度胁迫对银鳍幼鱼肝脏抗氧化酶、鳃和肾脏ATP酶活力的影响. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(4): 1059-1066] | |
| Zhao F, Zhuang P, Shi ZH, et al. A comparative analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in muscle of Pampus argenteus from four wild populations. Chinese Journal of Zoology, 2009, 44(5): 117-123 [赵峰, 庄平, 施兆鸿, 等. 银鲳4野生群体肌肉营养成分的比较分析与评价. 动物学杂志, 2009, 44(5): 117-123] | |
| Zhao F, Zhuang P, Zhang LZ, et al. Morphological variation of Pampus argenteus among five samples near the coastal area of the Bohai Sea, Huanghai Sea and East China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2011, 33(1): 104-110 [赵峰, 庄平, 章龙珍, 等. 渤海、黄海及东海近海五个银鲳地理群体的形态变异. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(1): 104-110] | |
| Zhao JL. A survey of karyotype study of marine and brackish water fish in China. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2000, 9(4): 344-347 [赵金良. 我国海水鱼和咸淡水鱼染色体组型研究概述. 上海海洋大学学报, 2000, 9(4): 344-347] | |
| Zhong SP, Chen C, Wang J, et al. Chromosome karyotype of sevenband grouper Epihephelus septemfasciatus. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2010, 17(1): 150-155 [钟声平, 陈超, 王军, 等. 七带石斑鱼染色体核型研究. 中国水产科学, 2010, 17(1): 150-155] | |
| Zhou LQ, Yang AG, Liu XZ, et al. The karyotype of the tonguefish Cynoglossus semilaevis. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2005, 29(3): 417-419 [周丽青, 杨爱国, 柳学周, 等. 半滑舌鳎染色体核型分析. 水产学报, 2005, 29(3): 417-419] | |
| Zhou LQ, Yang AG, Wu B, et al. A preliminary study on chromosome preparation and karyotype of humphead wrasse Cheilihus uhdulatus. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2010, 31(1): 54-58 [周丽青, 杨爱国, 吴彪, 等. 波纹唇鱼染色体制备及核型的初步研究. 渔业科学进展, 2010, 31(1): 54-58] | |
| Zhu XP, Lin MM, Li Z, et al. Search for peripheral blood lymphocytic cell cultivation and chromosome preparation in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Journal of Qingdao Aquaculture University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 24(4): 253-256 [朱香萍, 林明敏, 李桢, 等. 牙鲆外周血淋巴细胞的培养及染色体制备条件的探讨. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 24(4): 253-256] |



